A cube is a three-dimensional shape with six square faces, twelve edges, and eight vertices. It is one of the most familiar geometric solids and is a special type of rectangular prism where all sides are of equal length. A cube has a high degree of symmetry. Angles between its faces are right angles. It is often referred to as a “regular hexahedron”. Also cube is one of the Platonic […]
Posts with the keyword platonic solid
A dodecahedron is a three-dimensional polyhedron with twelve flat, regular pentagonal faces, twenty vertices, and thirty edges. It is one of the Platonic solids and is highly symmetrical, with each face being a regular pentagon. The dodecahedron’s shape is unique among the Platonic solids because its faces are polygons with five sides, unlike the others which have triangular faces. Due to its symmetry, the dodecahedron has been used in various […]
An icosahedron is a three-dimensional polyhedron with twenty triangular faces, twelve vertices, and thirty edges. It is one of the five Platonic solids and is highly symmetrical, with all faces being equilateral triangles. A regular icosahedron has equal edge lengths and angles between its faces, making it one of the most symmetrical shapes in three-dimensional space. In this short tutorial video, I am modeling and unrolling an icosahedron. I studied […]
An octahedron is a three-dimensional polyhedron with eight triangular faces, six vertices, and twelve edges. It is one of the Platonic solids and has high symmetry, with all of its faces being equilateral triangles. A regular octahedron can be visualized as two pyramids joined at their bases. It has the same number of faces as a cube has vertices, and the same number of vertices as a cube has faces. […]
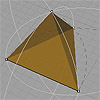
A tetrahedron is a three-dimensional shape with four triangular faces, four vertices, and six edges. It is the simplest polyhedron and, in its regular form, has equilateral triangles as faces, with all edges of equal length. Thus, known as one of the Platonic solids, a regular tetrahedron is highly symmetrical, and its shape is considered stable and efficient in many natural and man-made structures. In this short tutorial video, I […]
Here is a method for coding the dodecahedron and all its irregular variants in Grasshopper as quickly as possible. I utilized the golden ratio rectangles, usually used to construct the sister polyhedron, the icosahedron. However, the magic component of the Grasshopper, the Faceted Dome rescued me again to generate the dual of it, the dodecahedron. This is a special platonic solid, which has 12 regular pentagonal faces. There are several […]
Today, we have studied creating complex robot programs manually again. Platonic solids were the subject of this study. Students tried to create a sequence of robot moves that produces a Platonic solid out of a 17cm EPS cube. We simply call this the robotic hotwire cutting polyhedra exercise. However, the size of our hotwire cutter became one of the problems because of its risk of crashing. We crashed several times […]
Lokma is the name of a pastry made of fried dough soaked in sugar syrup or honey and cinnamon, typically shaped into a ring or ball. Unfortunately, it is not the “Lokma” we’ll study here. In Turkish, there is another meaning of the same word related to the history of Eastern architecture. It is the name of metal connectors in railings, mostly inside of the openings of garden walls and […]
This is the second year we are experimenting with a beautiful exercise with the Computation-based Basic Design 1 students at İstanbul Bilgi University Faculty of Architecture. The exercise is based on the ideas of Benay Gürsoy and Şebnem Yalınay, who are among the pioneers of this studio. The exercise is about the design and production of new year’s lanterns to be lit in the campus garden. Here are a few […]
I have come across several high school topics I was afraid of. While I was searching for a geodesic dome definition in Grasshopper, it was quite surprising that I found an easier way of modeling an approximation of icosahedron, the famous platonic solid. Icosahedron was a research topic of this website at various posts before (here, here, and here). In order to generate geodesic spheres, first I had to solve […]
The tetrahedron is a popular platonic solid for designers. We’ve explained how to draw them using equilateral triangles here before. Recently I’ve found (sorry, lost the web address) a much quicker way of modeling a Tetrahedron using a cube. It’s very simple, just connecting the three opposite corners of the cube automatically makes them equal, resulting in the four equal faces. Of course this time you’ll have to calculate the […]
I tried different approaches to drawing platonic solids using Grasshopper’s native components. However, it seems impossible now. In geometric definition, a platonic solid is a set of points, distributed on a sphere with equal distances. If the set contains 12 points, then it’s an icosahedron. I found lots of information about these objects and mathematicians seem to love analyzing them. They created different approaches to building an icosahedron. One of […]
An octahedron is a polyhedron and platonic solid with 8 faces of identical equilateral triangles. In this post, I will try to explain the drawing and unrolling process of the octahedron. It has a close relationship with the cube as it’s dual. In order to construct an octahedron, we first have to create a square. The main problem of drawing the square is determining the right angle (perpendicular axis) to […]
The dodecahedron is a Platonic Solid with 12 equilateral pentagonal faces. It has a close relationship with its 20-sided dual, Icosahedron. Mete Tüneri showed the following method of Dodecahedron construction, using only distances, corners of the pentagon, and a visionary equilateral triangle underneath. We’ll construct Dodecahedron, assuming that we’ve drawn an initial equilateral pentagon. We need to find out the pentagon’s angle of 3d rotation. First, put spheres at points a […]
Today’s polyhedra is the beautiful icosahedron. It is one of the five Platonic Solids with twenty equilateral triangular faces. Its dual is the dodecahedron, which has pentagonal faces. Here, I explained the process of modeling an icosahedron. After creating a regular pentagon, you should find the “tip” point of the Icosahedron by intersecting spheres from at least three of the corner points with a radius of the pentagon’s edges. You […]
The tetrahedron is a platonic solid with four equal triangular faces (equilateral), six equal edges, and four vertices. In the construction of a tetrahedron, we will look closer at length transfers using compass-like tools in two- and three-dimensional space. To define the edge length of the first triangle, start with any two points in Cartesian space. Using a compass (arc or circle), draw two arches (or circles) using your initial […]