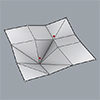
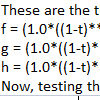We will try to create collapsible structures in this new series called Folding Experiments. In this example, we will be using Grasshopper and Kangaroo components to understand the Folding Experiments: Basics first. Like other projects, this is a Parametric Modeling course exercise that usually includes primary Grasshopper usage. In our first example, we will try to fold a mesh object. To be able to fold a surface like origami, we […]
Posts categorized under Research
The dwg format maps in Turkey are often problematic. You need to clean these for architectural studios. Maps mostly contain height information of buildings. But the contours of the buildings are distorted and polylines are generally exploded. The map of the region where we worked in the studio I conducted in the Fall 2021 term was also problematic. I created a Map Cleaner Script in Rhino Python and converted the […]
Architectural design, as a cognitive activity, has always been fed by architectural knowledge based onpractice and theory, and it has been questioned how creative and generative design processes canbenefit from scientific methods. Therefore, through inquiry and experimentation, the architect develops his or her ideas, constructs and analyzes the space, and continuously improves it. However, this is asubjective process. There are design tools and methods that provide objective criteria for theassessment […]
“Strange Start Startling Stop” was designed by Mary Purdy at the State University of New York in 1985. The composition is based on a hexagonal lattice (above figure). There are four prototiles, marking the four key moments in the shape-shifting process. The first prototile is a regular hexagon, which is also the first tile of the composition. This prototile morphs into a shape that is a composition of four smaller […]
This is the new paper with Meryem Nurefşan Yabanigül, published at Automation in Construction. It is also Meryem’s master’s thesis. This study is about testing the production of curved surfaces with non-linear robotic hotwire cutting and shape memory alloys. Below is the abstract of it: Robotic arms are being used by construction firms and schools of architecture around the world in design/build research and material studies. Some of these studies […]
In this session, I will add two new methods to the Vector class. I think this will finish the basics for the vectors. In the future, we are going to need several new methods like adding multiple vectors and interpolation. But for now, I think this would be sufficient to further advance into parametric curves and surfaces. These new methods will be based on the dot product method we created […]
This is the continuation of the Vector class we started here, and further advanced here, here, and here. This new Rhino Python implementation is mostly educational and partially a hobby. Before this session, we have developed display, magnitude, add, multiply, reverse, and subtract methods. This time, I am adding the vector normalization and dot product methods and seeing the utilizations of the dot product. Line Explanation 1-26 Already explained in […]
This is the continuation of the previous post on parametric curve equations. In this new version, the script picks a NURBS curve from the user. Then, it analyses the curve’s degree and control points. Unfortunately, only the curves with degree+1 number of control points can be processed. In the future, I hope that I will be able to extend this script to include multi-span curves with more than degree +1 […]
Today, I am going to make only one addition to the Vector class we recently started in Rhino Python. The magnitude of a vector can be easily calculated by assuming that the axes (2 or 3 axes) of it are perpendicular to each other. This gives us an opportunity to assume a right triangle visually, and calculate the magnitude (length) of a vector by using the Pythagorean Theorem. In short, […]
The parametric curve equations are good examples to demonstrate the bridge between computer-aided design and mathematics. Although useless and pointless, it is a good exercise to extract the curve equations. In this Rhino Python code, I present a generalized equation extractor for Rhino. Rhino curves are good examples de Casteljau and Bézier curves. You can see the mathematical underpinnings of Rhino curves with this exercise: This code asks the user […]
The SpaceChase plugin for Grasshopper focuses on initiating dynamic capabilities to Space Syntax theory by introducing the “Dynamic Canvas” model along with real-time editing capabilities in an interactive physics-based environment. SpaceChase is a software development project for “Mekan Dizimi Tasarım Uygulaması” under the ARDEB 1001 program of TÜBİTAK. It is a collaborative research project between İstanbul Technical University, İstanbul Bilgi University, and Tuşpa Design Studio. You can find more information about the project […]
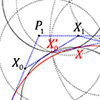
This is a new paper published in Nexus Network Journal. I tried to implement euclidean constructions by compass in the approximation of famous parametric curves; Bézier curves, and B-Splines. Then, I created the algorithms to calculate the number of steps on a compass-only construction of Bézier curves. I developed a simple Python script to simulate the geometric constructions. However, I have been studying this topic for nearly four years. In […]
This is the continuation of my new project of re-creating the parametric curve and surface methods of Rhino via Python scripting. If you remember, I started with the building block of vector operations, here and here. Then, I defined vector addition and multiplication, before going deeper into the geometric calculations. In fact, they are using the previously defined addition and multiplication methods. New Vector Operations: Subtraction and Reversing In the […]
Together with Sevde Dinçer, we published a new study on the digital reconstruction of muqarnas. This is also Sevde’s ongoing Ph.D. topic. Previously, she started studying muqarnas geometry in her master thesis under the supervision of Togan Tong. Then, she advanced her studies in this field. Eventually, my contribution to this study was about redefining and comparing the three major modeling approaches. Apart from that, the case study, literature research, […]
Today, I am going to advance the Vector class a bit more. Firstly, I will improve the display method I introduced recently. Then, I will add two new methods which handle the fundamental vector arithmetics in Rhino Python. Improving the Display Method In the previous attempt, I displayed vectors on the origin of the Rhino viewport. The coordinates of the tail of a vector are not stored within the object […]
Let’s continue from the Vector class that started yesterday. Previously, I defined this class to store three numbers (coordinates), named as “components”. I defined a method named __init__ for this. Similarly, I am adding a display method to the Vector class today. Note that I am using Rhino 6 in this code, but it should also work in Rhino 5 or 7. The code Below is the line-by-line explanation of […]
In this new series, I will be using Rhino Python to create some of the fundamental mathematical objects in Rhino. We will learn how to code in Python, and also try to get deeper into the intuition behind some of the fundamental concepts we use every day in Rhino and Grasshopper. The Vector class in Rhino Python is the starting point of this journey. Just like vectors, most of the […]
This is a simple inverse kinematics solution developed by Andreas Aristidou and Joan Lasenby in 2011. They call it Forwards and Backwards Reaching Inverse Kinematics (FABRIK in short). It was quite interesting the learn this technique because it is a fast and accurate approximation of a kinematic chain. There are very interesting potentials of this technique in terms of architectural simulations. I tried to develop a Rhino Python script in […]
I like to deal with possible small computational geometry problems. These fun games are taking 2-3 hours. In addition, these are also memorable exercises. I was reviewing the Anemone plugin last week. I noticed that the Golden Ratio in Grasshopper was not geometrically generated before. Some of the greatest mathematical minds of all ages, from Pythagoras and Euclid in ancient Greece, through the medieval Italian mathematician Leonardo of Pisa and the Renaissance astronomer Johannes Kepler, to present-day scientific […]
This is a robotic fabrication student project developed in the Digital Fabrication elective course in 2018. This group of students experimented with the hot wire cutting of EPS foam. Their aim was to create curved surfaces by using a straight wire. Design research started with a literature study of precedents. Then, after several cutting experiments with the available hotwire cutter tool, they gained better control over the technology. However, they […]