Canopy of Vector Fields
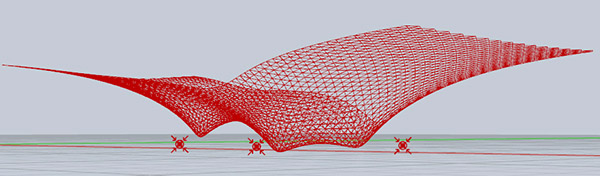
Utilizing “Force Field” components of Grasshopper to show my students how it is easy to develop flexible surfaces in design. The classical parametric canopy design is introduced in this video:
According to Wikipedia;
In vector calculus, a vector field is an assignment of a vector to each point in a subset of space.[1] A vector field in the plane, for instance, can be visualized as a collection of arrows with a given magnitude and direction each attached to a point in the plane. Vector fields are often used to model, for example, the speed and direction of a moving fluid throughout space, or the strength and direction of some force, such as the magnetic orgravitational force, as it changes from point to point.
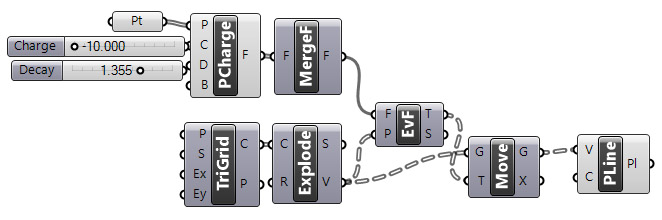
This file [GHX: 0.9.0076] is the Grasshopper definition.