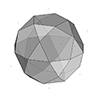
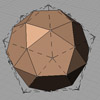
In geometry, a truncated icosidodecahedron, rhombitruncated icosidodecahedron, great rhombicosidodecahedron, omnitruncated dodecahedron, or omnitruncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid. It is one of thirteen convex, isogonal, non-prismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces. In this short tutorial, I am constructing an irregular truncated icosidodecahedron. It is not the regular Archimedean solid, but a rough approximation of it. I made this model to exercise the exploration of […]
Search results for ‘dodecahedron’
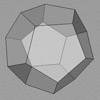
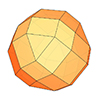
The rhombicosidodecahedron, an Archimedean solid, is one of the 13 convex polyhedra made up of regular polygons. While all its faces are congruent, they consist of various types of regular polygons. I previously explored this fascinating polyhedron and am revisiting it now as part of the Architectural Geometry course. In this short tutorial video, I demonstrate the modeling of a rhombicosidodecahedron. Despite its lengthy and unusual name, this polyhedron is […]
In geometry, the excavated dodecahedron is a star polyhedron that looks like a dodecahedron with concave pentagonal pyramids in place of its faces. In this short tutorial video, I am modeling an excavated dodecahedron in the Rhinoceros software. I use basic drawing and modeling commands. I aim to introduce this skill to beginner-level architects and designers. As the name suggests, this process includes the construction of the dodecahedron first. Then, […]
An icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron that is part of the family of Archimedean solids. It has 32 faces, consisting of 12 regular pentagonal faces of a dodecahedron and 20 regular triangular faces of an icosahedron. It is highly symmetrical, with the same arrangement of faces around each vertex. In this short tutorial video, I am modeling and unrolling an icosidodecahedron. This polyhedron is very interesting and is mostly used as […]
A dual polyhedron is a concept in geometry where two polyhedra are related in such a way that the vertices of one polyhedron correspond to the faces of the other, and the faces of the first polyhedron correspond to the vertices of the second. The process of creating a dual polyhedron is called duality, and it applies to many regular, semi-regular, and some irregular polyhedra. In the case of Platonic […]
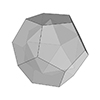
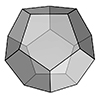
A dodecahedron is a three-dimensional polyhedron with twelve flat, regular pentagonal faces, twenty vertices, and thirty edges. It is one of the Platonic solids and is highly symmetrical, with each face being a regular pentagon. The dodecahedron’s shape is unique among the Platonic solids because its faces are polygons with five sides, unlike the others which have triangular faces. Due to its symmetry, the dodecahedron has been used in various […]
Modeling a rhombicosidodecahedron requires exploding and extending the faces of a dodecahedron and an icosahedron of the same edge length. We begin with both polyhedra centered at the same point. Then, we explode the faces of the dodecahedron and icosahedron outward from the center. We extend their planes while maintaining their orientation and shape. As these faces extend, they intersect and form new polygonal regions. Triangular and pentagonal faces emerge […]
An Archimedean solid is a convex isogonal (vertex-transitive) and nonprismatic solid that is composed of two or more regular polygonal faces. There are thirteen such solids in geometry. Coding the snub dodecahedron study aims to generate one of these solids, composed of 12 regular pentagons, and 80 regular triangles. You can generate the snub dodecahedron by expanding and twisting the faces of a dodecahedron outward. This also creates rhombicosidodecahedron, which […]
Here is a method for coding the dodecahedron and all its irregular variants in Grasshopper as quickly as possible. I utilized the golden ratio rectangles, usually used to construct the sister polyhedron, the icosahedron. However, the magic component of the Grasshopper, the Faceted Dome rescued me again to generate the dual of it, the dodecahedron. This is a special platonic solid, which has 12 regular pentagonal faces. There are several […]
This is a 3d modeling tutorial for the platonic solid of dodecahedron. Modeling a dodecahedron is a good exercise for the basic transformation commands such as Rotate3D in Rhinoceros. You will see that it is possible to calculate the rotation angle by using sphere intersections. I learned this elegant method while teaching Architectural Geometry classes 12 years ago. It is based on the fact that, given a rotation axis and […]
The dodecahedron is a Platonic Solid with 12 equilateral pentagonal faces. It has a close relationship with its 20-sided dual, Icosahedron. Mete Tüneri showed the following method of Dodecahedron construction, using only distances, corners of the pentagon, and a visionary equilateral triangle underneath. We’ll construct Dodecahedron, assuming that we’ve drawn an initial equilateral pentagon. We need to find out the pentagon’s angle of 3d rotation. First, put spheres at points a […]
Icosidodecahedron is an Archimedian Solid, a thing in between the Platonic Solids of Icosahedron (d20) and Dodecahedron (d12). It is a rectified version of an Icosahedron, constructed by dividing every edge into two equal segments and joining these segments to create a composition of equilateral pentagons and triangles. Archimedian Solids consist of at least two equilateral polygons, whereas Platonic Solids are constructed by only one. We’ll deduce an Icosidodecahedron from […]
I had been researching Goldberg Polyhedra for a while. While exploring how to perform chamfer operations in Grasshopper, I found some interesting results. I want to share them with you. In this Grasshopper project, I reused my previous work, where I built a dodecahedron using the golden ratio. Essentially, all I did was add the Fillet Edge component. I don’t use this component much, so I learned it through this […]
Buckminster Fuller used the term “dymaxion” for a variety of his designs, and one of these was the dymaxion map. It was based on the geometry of a polyhedron. While the dymaxion map is more directly related to the icosahedron, Fuller’s work often involved using other polyhedral shapes. One of them is the cuboctahedron. He used this term for various conceptual and practical designs, particularly in the context of his […]
The regular dodecahedron is one of the five Platonic solids, characterized by having 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 vertices, and 30 edges. When you elongate it, you extend its structure in one or more directions, resulting in a shape that retains the basic properties of the dodecahedron but is stretched out. The elongated dodecahedron might not catch your eye at first—it’s just a long version of a shape you’ve probably […]
The rhombic dodecahedron is a polyhedron with twelve rhombus-shaped faces, where each face has four sides of equal length. It is possible to construct the space-filling variant of the rhombic dodecahedron by arranging multiple such rhombic dodecahedra in a regular pattern so that they fill space without leaving any gaps. In his 1611 work on snowflakes titled “Strena seu de Nive Sexangula,” Johannes Kepler observed that honey bees utilize the […]
The Polyhedra Unroller with Flaps is a simple tool I developed for the obvious purpose. It picks any polyhedra (closed polysurface) from the user and unrolls it flat on the XY plane. This part is easy because a short Python script is sufficient. The important function of the script is the generation of the production drawings from the unrolled net. It means, the generation of the flaps. Here, the continuous […]