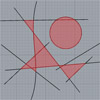
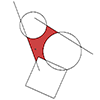
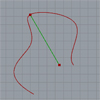
Again, I continue with some simple solutions for Grasshopper. The surface split component gives all possible surfaces sliced with given curves. And it creates “invalid” curves with at least one open edge. I used this to perceive the closed regions within a given complex curve set. Just put the “Clean” component to erase the outer invalid surfaces and there remain the closed ones. However this time the question was where […]
August 2013
This is a simple trick that shows the utilization of the “surface split” component in Grasshopper. It is used for detecting the inner regions of any given two-dimensional linework. Thus, it resembles the hatch boundary detection of AutoCAD and similar software. There is no built-in hatch component in Grasshopper. But maybe you can use this as a starting point if you want to develop it. The definition starts with drawing […]
Today’s tip is about two-dimensional curve-point calculations. It is very handy to use “closest point” components in Grasshopper. You can calculate distances and directions between curves, surfaces, and points. Then, place point objects in relation to the proximity of another object. However, there is no “farthest point” implemented yet. I tried to calculate the farthest point from a curve. First, I tried to translate the curve in a fashion that […]
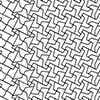
It has been a while since I didn’t post any patterns. Here is a beautiful one from the iconic design studio of William Huff. Crossover Parquet Deformation is a single-axis, line-based deformation algorithm, constructed on a regular quadrangular hyperframe, designed by Richard Lane at the Basic Design studio of William Huff in 1963. It presents two different parquet deformation sequences linked together. Thus, the designer created a transition between the […]